THE Energy Commission (EC) had in May 2025 launched a tender for gas-based power generation capacity.
The tender involves gas-based power generation supply from two categories, namely new capacity as well as extension/expansion of expiring/recently expired capacity.
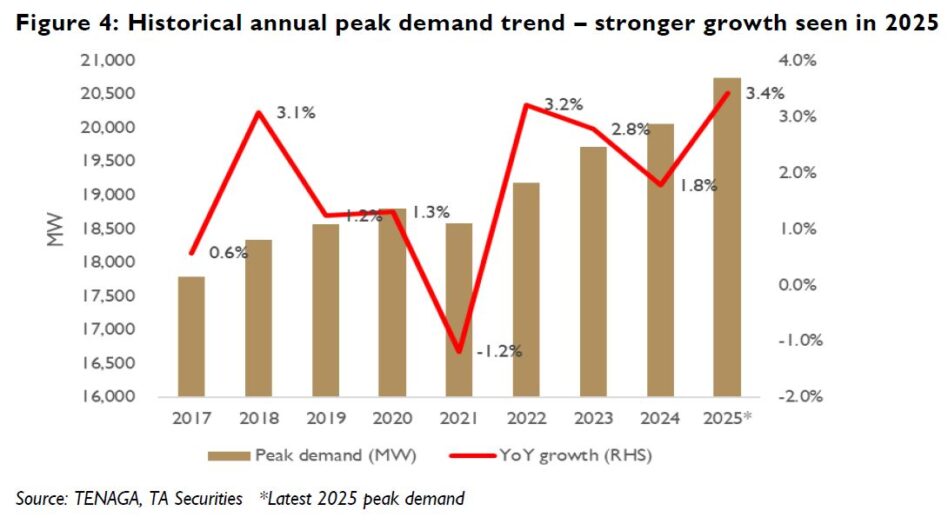
A total of 8GW capacity is understood to be on offer with scheduled commissioning targets between 2025 and 2029, whereby a significant portion of the auctioned capacity is understood to be required between 2026 and 2027.
Key frontrunners include MALAKOF and TENAGA backed by their strong track record and suitable sites that are readily connected to the grid and gas pipelines from expiring or expired power plants.
Other potential contenders include PETGAS as well as non-listed Edra Energy and Teknologi Tenaga Perlis.
“We believe the result of the tender, likely to trickle in by year-end, will be a key investor focus in the second half of 2025,” said TA.
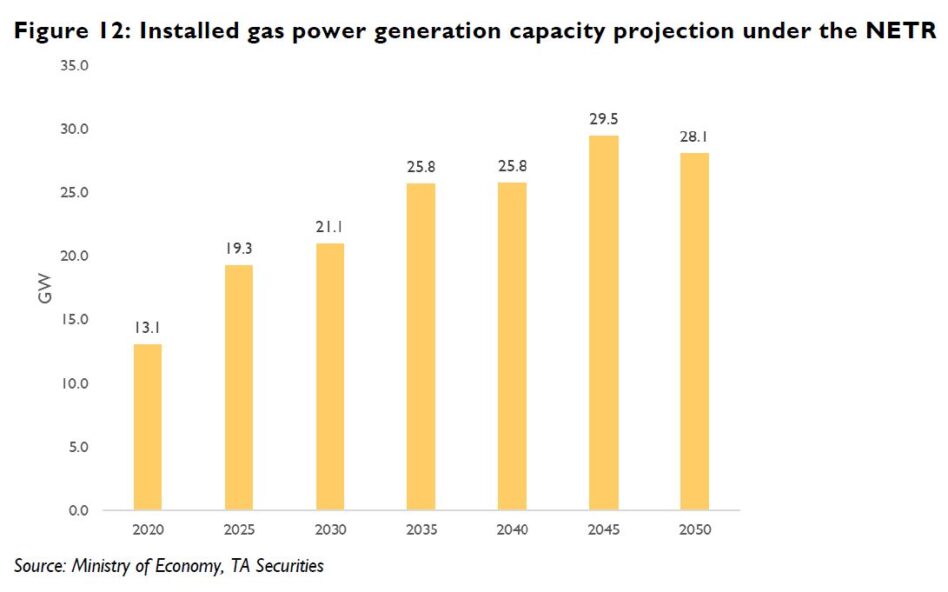
In line with the significant build-up of gas generation capacity, we believe an increase in natural gas demand, in turn, requiring an expansion in gas supply infrastructure, is imminent.
“We believe expansion of RGT capacity alongside gas transportation pipelines will be a key focus within the gas utilities sub-sector,” said TA.
Given strong policy backing and the NETR’s aggressive 70% RE mix target by 2050, the transition to RE remains a key theme for the P&U sector.
The record RE capacity rollout over the next 2 years is likely to drive order books and revenues of RE EPCC players to new highs.
The Regulatory Period 4 (RP4) (2025-2027) determination saw a broadly positive outcome for TENAGA, which underpinned our earlier thesis of a step-up in grid spending.
A key positive was the +29% increase in base allowable capital expenditure (capex) to RM26.55 bil, which rises to RM42.82 bil (+108%) if contingent capex of RM16.27 bil is triggered within the period.
In aggregate, the total RP4 (base & contingent) capex is fairly well distributed between energy transition, demand growth and security of supply requirements.
TENAGA has indicated that it is confident of utilizing at least 60-70% of RP4 contingent capex underpinned by the need to address the strong demand growth and aggressive energy transition plans.
The step-up in grid capex is expected to expand TENAGA’s regulated asset base and ultimately drive TENAGA’s regulated earnings growth moving forward.
Following the setting up of Energy Exchange Malaysia (ENEGEM) in April 2024 followed by an inaugural auction to potential offtakers in June 2024, Malaysia’s pilot RE export took off in December 2024 with the signing of a Renewable Energy Supply Agreement between TENAGA and Sembcorp Industries.
The agreement entails the supply of 50MW RE of a total 100MW allocated under the pilot phase of ENEGEM.
RE supply for the pilot phase of ENEGEM is currently limited to existing solar and hydro resources, but TA believes this will later be expanded to new RE sources, in line with the objective to spur investments into domestic RE capacity and technologies.
“In this regard, we believe RE exports will eventually create capacity growth opportunities for domestic RE players, capitalizing on Malaysia’s geographical proximity to the region’s key demand centre in Singapore,” said TA.
“As the national grid monopoly, we believe TENAGA stands to benefit from any investments into regional interconnection involving integration with the Peninsular Malaysia grid,” said TA.
TA re-affirms their overweight stance on the P&U sector premised on:
(i) Demand-supply tightness in the generation market.
(ii) Record RE rollout.
(iii) A step-up in grid capex to accommodate the energy transition and demand growth.
(iv) Potential expansion of gas supply infrastructure.
(v) Potential nuclear addition to the energy mix. —June 18, 2025
Main image: KPMG International