MALAYSIA’s economic expansion continued in quarter four 2024 (4Q24) albeit at a moderated pace of 5.0% year-on-year (yoy), compared to 5.3% in the previous quarter beating market consensus.
“This brings the country’s full-year gross domestic product (GDP) growth to 5.1%, a notable improvement from 3.6% in 2023 driven by resilient domestic demand, steady expansion in services and manufacturing, and robust construction activity,” said APEX Securities in the recent Economic Update Report.
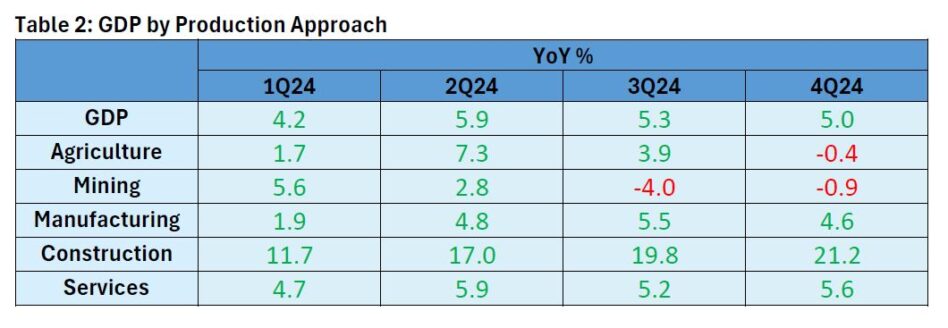
While the economy remains on a positive trajectory, challenges such as weaker agricultural output and a slower growth rate in the mining sector tempered overall growth.
On a quarter-on-quarter (qoq) basis, Malaysia’s GDP decreased by -1.1% in 4Q24, down from 1.9% in 3Q24.
The moderation was largely influenced by a decline in all sectors except for mining which expanded to 5.9% qoq (3Q24: -1.1% qoq) marking the first growth after three quarters of contraction.
The construction sector saw a contraction of -2.3% after strong growth in 3Q24 at 5.7% amid global economic uncertainties may have led to delays in project initiations.
Notably, the manufacturing sector declined to -2.8% reversing the 1.9% growth seen in 3Q24, likely due to weak global demand.
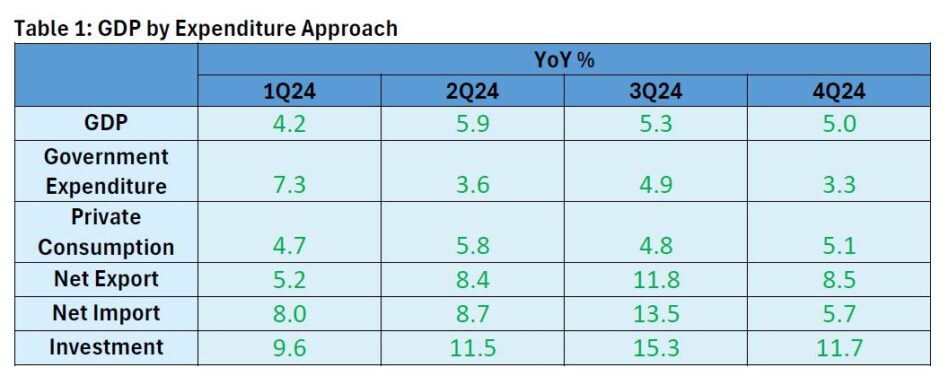
Private consumption grew by 5.1% in 4Q24 (3Q24: 4.8%), supported by increased spending on transport, restaurants & hotels, and food & non-alcoholic beverages.
Meanwhile, government expenditure rose by 3.3%, slowing from 4.9% in the previous quarter, driven by higher spending on supplies and services.
For the full year 2024, private consumption expanded by 5.1% (2023: 4.7%), while government expenditure increased by 4.7% (2023: 3.3%).
The construction sector maintained its robust expansion, growing by 21.2% yoy (3Q24: 19.8%).
The expansion was driven by strong growth across all segments, particularly in non-residential buildings and specialised construction activities, which recorded double-digit increases of 23.9% (3Q24: 28.1%) and 23.6% (3Q24: 21.7%), respectively.
This reflects strong investor confidence and the government’s commitment to infrastructure development.
Multi-year projects under the Economy MADANI framework, including the National Energy Transition Roadmap (NETR) and the New Industrial Master Plan (NIMP) 2030, are anticipated to sustain growth momentum in 2025.
Additionally, residential buildings saw a sharp rise of 30.3% (3Q24: 22.7%), while civil engineering grew by 9.1%, slightly lower than 10.7% in the previous quarter.
For the full year 2024, the construction sector posted a robust expansion of 17.5%, significantly higher than the 6.1% growth recorded in the previous year.
Looking ahead, Malaysia’s economy is expected to grow at a more normalised pace of 4.6% in 2025.
Key growth drivers include sustained infrastructure investments under the 12MP will continue boosting the construction sector, particularly in energy, transportation, and digital infrastructure.
“We anticipate household spending to remain resilient amid rising wages and a strong labor market will support domestic consumption, although inflationary pressures from subsidy rationalization may pose some challenges,” said APEX.
Besides that, APEX hopes that the easing of global monetary policies and steady demand from key trading partners should help Malaysia’s export sector remain competitive.
Despite the optimistic outlook, Malaysia’s growth trajectory is not without risks.
Globally, APEX continues to monitor external trade uncertainties such as geopolitical tensions, protectionist policies, and tariff escalations which could dampen export demand.
Furthermore, global interest rate adjustments could influence capital flows and currency stability, affecting investment sentiments.
Domestically, inflationary pressures remain amid subsidy retargeting particularly affecting the T15 income group, may impact discretionary spending though overall inflation is projected to remain manageable at 2.4% in 2025. —Feb 17, 2025
Main image: Malaysia Travel









